Mental Health Concepts
Mental Health Concepts
Understanding Mental Health and Wellness

Mental health encompasses our emotional, psychological, and social well-being. It affects how we think, feel, and act, as well as how we handle stress, relate to others, and make choices. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), mental health is not merely the absence of mental illness but a state of well-being in which every individual realizes their potential, can cope with the normal stresses of life, can work productively, and is able to contribute to their community.
Mental health can be divided into several key dimensions:
- Emotional Well-Being: This involves understanding and managing emotions, coping effectively with stress, and maintaining a positive self-image. Emotional well-being allows individuals to navigate life’s challenges with resilience.
- Psychological Well-Being: This dimension relates to personal growth, purpose in life, and self-acceptance. It includes the ability to form positive relationships and maintain a sense of autonomy.
- Social Well-Being: Social connections are vital for mental health. This dimension involves having supportive relationships, a sense of belonging, and the ability to engage with the community.
- Spiritual Well-Being: This dimension encompasses personal beliefs, values, and a sense of purpose. Spiritual well-being can contribute to overall mental health, as it often provides individuals with strength during difficult times.
- Understanding the Impact of Mental Health on Overall Well-Being
Mental health is integral to overall health. It affects physical health, relationships, productivity, and quality of life. Individuals with poor mental health may experience:
- Physical Health Problems: There is a strong connection between mental and physical health. Chronic stress and mental illnesses can lead to physical health issues, such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and obesity. For example, individuals with depression may neglect self-care and exercise, leading to deteriorating physical health.
- Impaired Social Relationships: Mental health conditions can strain relationships with family, friends, and colleagues. Stigmatization and withdrawal from social activities may exacerbate feelings of isolation and loneliness.
- Reduced Quality of Life: Individuals struggling with mental health issues may experience decreased life satisfaction and enjoyment. They may find it challenging to engage in meaningful activities, affecting their overall well-being.
- Impact on Productivity: Mental health conditions can hinder cognitive functioning, leading to decreased focus and productivity. This can have implications for work performance, job retention, and career advancement.
Recognizing the importance of mental health is essential for promoting wellness and preventing mental health disorders. Early intervention and support can mitigate the impact of mental health issues and lead to improved outcomes.
Classification of Mental Health Disorders
The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition (DSM-5), serves as the authoritative guide for diagnosing mental health disorders. It classifies disorders based on specific criteria, enabling mental health professionals to provide accurate diagnoses and appropriate interventions.
The DSM-5 categorizes mental health disorders into various classes, including:
- Mood Disorders: These include major depressive disorder, bipolar disorder, and persistent depressive disorder (dysthymia). Mood disorders are characterized by disturbances in emotional regulation.
- Anxiety Disorders: Common anxiety disorders include generalized anxiety disorder, panic disorder, social anxiety disorder, and specific phobias. These disorders involve excessive fear or anxiety that impacts daily functioning.
- Psychotic Disorders: Schizophrenia is the primary psychotic disorder characterized by distorted thinking, hallucinations, and impaired functioning. Psychotic disorders significantly affect an individual’s perception of reality.
- Personality Disorders: These include borderline personality disorder, narcissistic personality disorder, and antisocial personality disorder. Personality disorders involve enduring patterns of behavior, cognition, and inner experience that deviate from cultural expectations.
- Substance-Related Disorders: Substance use disorders are characterized by the harmful consequences of substance use, including addiction and withdrawal symptoms.
- Neurodevelopmental Disorders: These disorders, including autism spectrum disorder and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), typically manifest in childhood and affect cognitive and emotional development.
- Trauma- and Stressor-Related Disorders: Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and acute stress disorder fall under this category. They arise from exposure to traumatic events and can lead to persistent psychological distress.
Understanding the Continuum from Mental Wellness to Mental Illness
Mental health exists on a continuum, ranging from optimal mental wellness to severe mental illness. This continuum emphasizes that mental health is not a binary concept; individuals can experience varying degrees of mental health throughout their lives.
- Mental Wellness: At the wellness end of the continuum, individuals demonstrate resilience, coping skills, and positive emotional well-being. They can effectively manage stress, maintain healthy relationships, and engage in fulfilling activities.
- Mild Distress: This stage may involve temporary feelings of anxiety or sadness but does not significantly impair functioning. Individuals may experience stress due to life changes, but they often employ coping strategies to manage these feelings.
- Moderate Distress: In this stage, individuals may experience persistent symptoms that affect daily functioning. They might struggle with concentration, motivation, or relationships. This stage often requires intervention to prevent further deterioration.
- Severe Mental Illness: Individuals at this end of the continuum may experience debilitating symptoms that hinder their ability to function in daily life. Severe mental illnesses may require intensive treatment and support to manage symptoms effectively.
Understanding this continuum is essential for healthcare providers, as it highlights the need for early intervention and the promotion of mental wellness. By addressing mental health concerns at any stage, providers can help individuals maintain optimal mental health and prevent the escalation of mental health disorders.
Promoting Mental Wellness and Resilience Strategies
Discussing the Role of Physical Health, Social Connections, and Purpose
Promoting mental wellness involves recognizing the interconnectedness of various aspects of life. Key factors that contribute to mental wellness include:
- Physical Health: Physical activity, a balanced diet, and adequate sleep significantly impact mental health. Regular exercise releases endorphins, improves mood, and reduces symptoms of anxiety and depression. A nutritious diet supports brain function and emotional regulation, while sufficient sleep enhances cognitive abilities and emotional resilience.
- Social Connections: Strong social support networks are crucial for mental wellness. Positive relationships with family, friends, and community members foster a sense of belonging and support individuals through challenging times. Engaging in social activities and maintaining connections can reduce feelings of isolation and loneliness.
- Purpose and Meaning: Having a sense of purpose in life contributes to mental wellness. Engaging in meaningful activities, whether through work, hobbies, or volunteerism, enhances self-esteem and fosters a sense of accomplishment. Individuals who feel connected to a greater purpose often report higher levels of happiness and life satisfaction.
Implementing Resilience Strategies
Building resilience is a proactive approach to mental wellness. Resilience strategies can include:
- Mindfulness and Meditation: Practicing mindfulness and meditation helps individuals stay present, manage stress, and enhance emotional regulation. These practices can reduce anxiety and promote a sense of calm.
- Cognitive-Behavioral Techniques: Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) techniques can help individuals identify and challenge negative thought patterns, fostering a more positive outlook and effective coping strategies.
- Stress Management: Developing effective stress management techniques, such as time management, relaxation exercises, and assertiveness training, empowers individuals to cope with life’s challenges.
- Seeking Professional Support: Encouraging individuals to seek professional help when needed is essential for mental wellness. Therapists, counselors, and support groups can provide valuable resources and guidance.
By promoting mental wellness and resilience strategies, healthcare providers can support individuals in maintaining their mental health and enhancing their quality of life.
Incorporating Research-Supported Interventions into Care Plans
Evidence-based practice (EBP) is a cornerstone of nursing and healthcare. It involves integrating the best available research evidence with clinical expertise and patient values to inform decision-making in patient care.
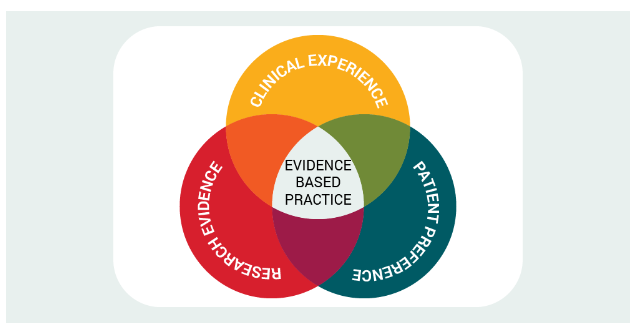
- Understanding the EBP Process: The EBP process typically involves identifying a clinical question, conducting a literature review, evaluating the quality of evidence, and applying findings to practice. Nurses must stay informed about current research and developments in mental health care to implement effective interventions.
- Implementing Evidence-Based Interventions: Research-supported interventions may include cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) techniques for managing anxiety, psychoeducation for individuals with mood disorders, and mindfulness practices for stress reduction. Tailoring these interventions to individual patient needs enhances their effectiveness.
- Monitoring Outcomes: Evaluating patient outcomes is critical for assessing the effectiveness of interventions. Nurses should document and analyze the impact of implemented strategies on patients’ mental health and overall well-being. This continuous feedback loop informs future care and adjustments to treatment plans.
Understanding the Importance of Individualized Care
Individualized care is essential in mental health nursing. Recognizing that each patient is unique, with different experiences, preferences, and needs, is vital for effective treatment.
- Holistic Assessment: Comprehensive assessments should consider physical, emotional, psychological, social, and spiritual dimensions. Understanding a patient’s background, cultural beliefs, and personal experiences informs care planning.
- Collaboration with Patients: Involving patients in their care planning fosters a sense of ownership and empowerment. Collaborating with patients to set goals and develop treatment plans enhances motivation and adherence to interventions.
- Cultural Competence: Mental health care must be culturally sensitive and tailored to diverse populations. Understanding cultural beliefs and practices helps nurses provide appropriate care and reduce barriers to treatment.
Encouraging Patient Empowerment and Goal-Setting
Recovery-oriented approaches emphasize the importance of empowering individuals in their mental health journey. This paradigm shift from traditional treatment models to recovery-oriented practices recognizes that individuals can manage their conditions and lead fulfilling lives.
- Encouraging Self-Management: Patients should be encouraged to take an active role in their recovery. Providing education about mental health conditions, treatment options, and self-care strategies empowers individuals to make informed choices.
- Goal-Setting: Collaborating with patients to set realistic and achievable goals fosters motivation and a sense of accomplishment. Goals may focus on various aspects of life, including personal growth, relationships, and vocational aspirations.
- Building Skills: Equipping patients with coping skills and strategies for managing symptoms is crucial. Skills training in areas such as communication, problem-solving, and stress management enhances individuals’ ability to navigate challenges.
Recognizing the Significance of Peer Support in Recovery
Peer support plays a vital role in recovery-oriented approaches. Connecting individuals with others who have lived experience fosters a sense of belonging and reduces feelings of isolation.
- Peer Support Programs: Integrating peer support programs into mental health care provides individuals with valuable resources. Peer specialists can share their experiences, offer guidance, and help individuals navigate the recovery process.
- Community Support: Encouraging participation in community support groups and organizations enhances social connections and provides ongoing support. These groups offer a safe space for individuals to share their experiences and receive encouragement.
- Reducing Isolation: Peer support can help reduce the stigma associated with mental illness. Sharing personal stories and experiences fosters understanding and compassion, creating a supportive environment for recovery.
Understanding the Impact of Stigma
Stigma surrounding mental health can significantly impede individuals from seeking treatment and support. Addressing stigma is a crucial aspect of promoting mental health and well-being.
- Understanding Types of Stigma: Stigma can be categorized into public stigma (societal attitudes) and self-stigma (internalized beliefs). Public stigma can lead to discrimination, while self-stigma may result in feelings of shame and decreased self-worth.
- Educational Initiatives: Promoting mental health awareness and education is essential for reducing stigma. Public campaigns, workshops, and community outreach can help dispel myths and misconceptions about mental health conditions.
- Advocacy and Policy Change: Advocating for policy changes that protect individuals with mental health conditions is vital. This includes promoting equal access to mental health services, anti-discrimination policies, and resources for education and support.
Promoting Awareness and Education to Reduce Discrimination
Education is a powerful tool in combating stigma and discrimination associated with mental health. By increasing awareness, society can foster a more inclusive and supportive environment for individuals with mental health conditions.
- Training for Healthcare Providers: Providing education and training for healthcare providers on mental health issues and stigma can enhance their ability to offer compassionate care. Understanding the impact of stigma on individuals can improve patient-provider interactions.
- Community Involvement: Engaging communities in discussions about mental health can foster understanding and acceptance. Community events, workshops, and support groups can promote dialogue and create a supportive network.
- Empowering Individuals: Encouraging individuals to share their stories and experiences can humanize mental health issues and reduce stigma. Personal narratives can inspire others and promote empathy within the community.
Conclusion
Understanding mental health concepts is essential for nursing practice, particularly within the psychosocial integrity framework. By recognizing the importance of mental health, the spectrum of mental health conditions, and the strategies for promoting mental wellness, nurses can provide holistic and individualized care.
Utilizing evidence-based practices, implementing recovery-oriented approaches, and addressing stigma are integral components of effective mental health care. By fostering an environment of understanding, support, and empowerment, nurses can positively impact the mental health and well-being of their patients.
